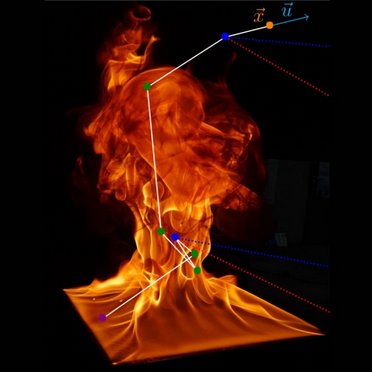
A new project under the Inria Quadrant Program (PIQ) funded by France 2030, the RAYFLAM project proposes a new approach to fire simulation that incorporates a Monte Carlo-type formulation of flame radiation.
Thermal radiation plays a decisive role in the spread of fire. However, taking it into account in numerical simulations remains a real challenge: its physical complexity, the extent of the time and space scales, and the precision required for full-scale scenarios are all scientific obstacles.